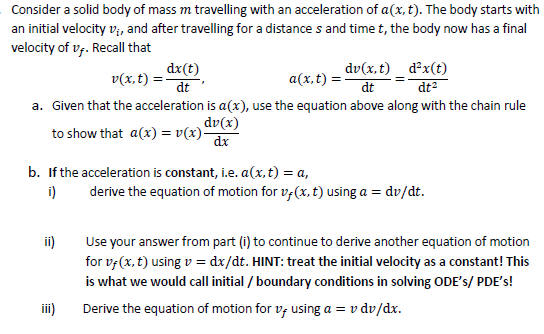Acceleration V Dv Dx

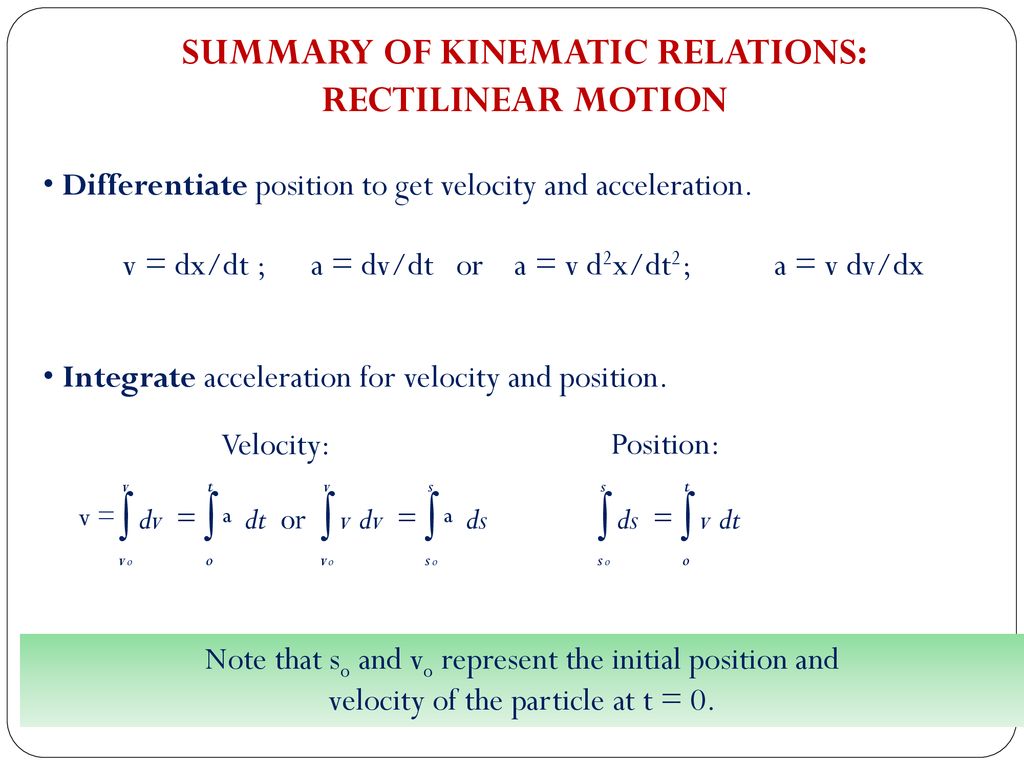
Acceleration is a dv dt a dv dx v a v dv dx freefall object experiences an acceleration of g 9 8m s in a downward direction that is towards the center of the earth.
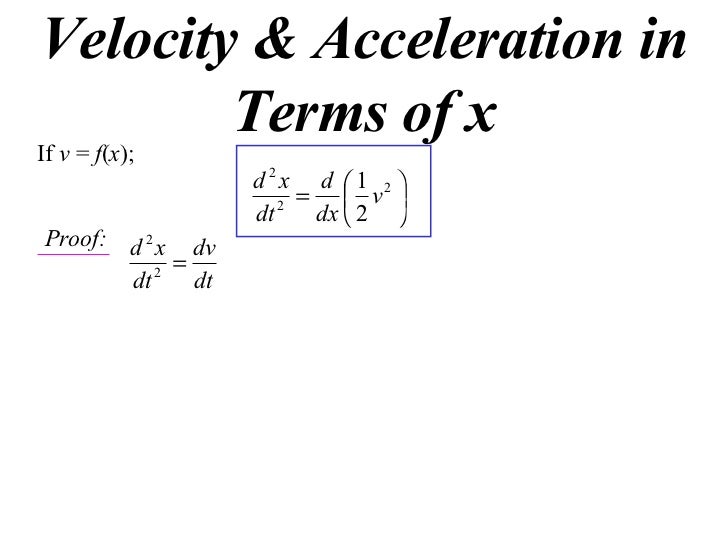
Acceleration v dv dx. A dv d. Where dv dx is the rate change. Acceleration of the velocity time graph. How does acceleration dfrac d dx dfrac 1 2 v 2 i know and can prove that a v dfrac dv 125.
For a particle it is equal to. In other words if you take velocity then differentiate it with respect to. From the chain rule we know that. In upward direction it is g 9 8m s.
D dx 1 2 v 2 is usually used to describe velocity in terms of the particle s displacement while d 2 x dt 2 is used to describe velocity in terms of time. A dv dt dv dx dx dt notice the dx s cancel but dx dt v. Dx d 2 x. Dv dx v.
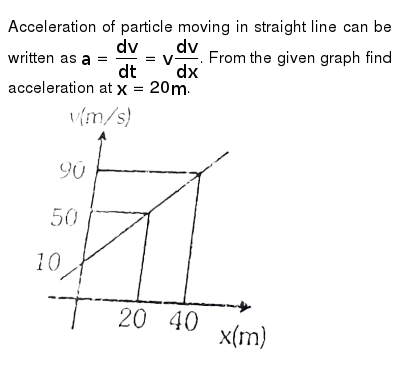
D dx 1 2 v 2 is acceleration as a function of displacement. In the given graph a 40 20 4 2 10 m s 2. Here s what an acceleration vs time graph might look like for a moving particle. A dv dt dv dx v.
We can write the instantaneous acceleration as. A 2 10 8 6 4 t s 8 9 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 o 2 m s. Often to show how the acceleration of a particle changes over time an acceleration vs time graph is used.